
Vedantu LIVE Online Master Classes is an incredibly personalized tutoring platform for you, while you are staying at your home. Total area of hexagonal faces = \ respectively. Let a hexagonal prism with height h and base side a, then The surface area of a hexagonal prism is the sum of the area of 6 rectangular faces and the 2 hexagonal faces. For a 3D figure, we individually calculate the area of each face and add them up to get the total surface area.

The surface area is defined as the quantity that expresses the extent of a 2-D figure or planar lamina.

The different shapes in geometry can be measured using different measures like area volume, perimeter, etc. The diagonals intersect each other at the center point.Īll the angles are equal in a regular prism while the angles are different in an irregular prism. The rest of the 6 faces are rectangular in shape. The hexagonal prism has 8 faces, 12 vertices, and 18 edges. The hexagonal prism has 8 faces: 2 - hexagonal, top and bottom 6 rectangular side faces The edges are the line segments that act as an interface between two faces. The faces are the individual flat surfaces of a solid. The vertex is a point where two edges meet. The number of faces, edges and vertices defines any 3-dimensional figure. Hexagonal Prism Faces, Edges and Vertices
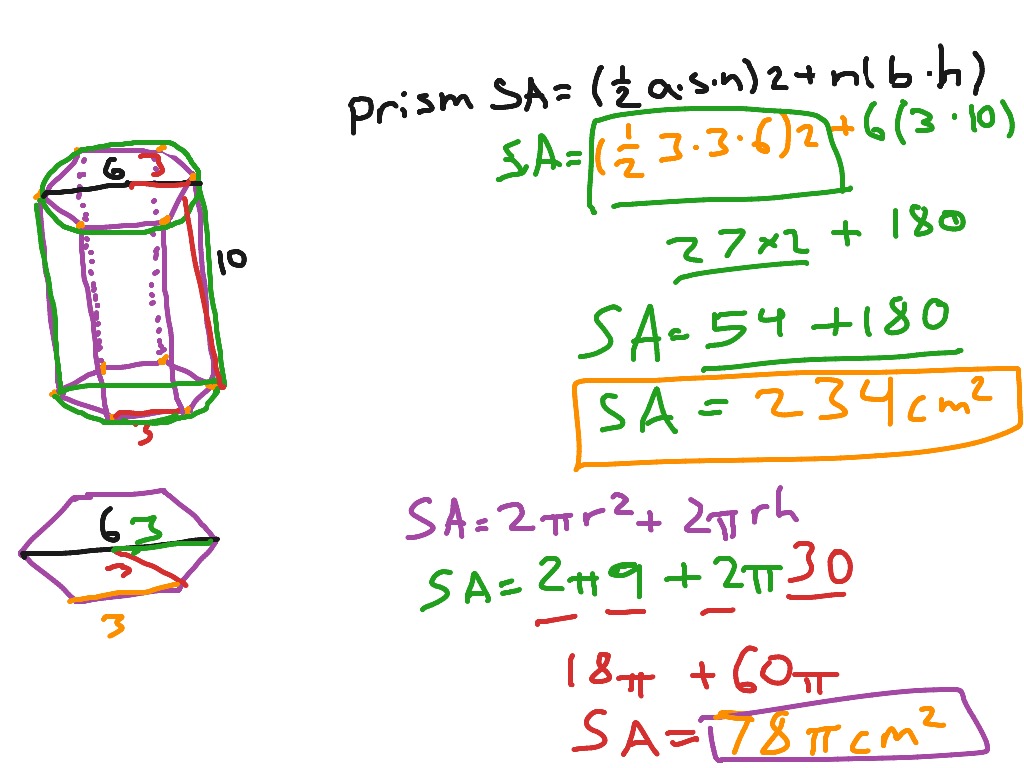
An irregular hexagonal prism does not have sides with the same length and same angles. A regular hexagonal prism has a hexagonal-shaped base of the same length. There can be two types of hexagonal prisms, that is, regular and irregular prisms. It has 8 faces, of which 2 are hexagonal, the top and bottom faces, and the rest 6 faces are rectangular. Some real-life examples of hexagonal prisms are nuts, pencils, weights etc. It is a 3D polyhedron having 2 hexagonal bases and 6 rectangular faces. If the faces are not perpendicular to the bases, it is called an oblique prism.Ī prism with bases in a hexagon shape is called a hexagonal prism. If the faces are rectangular and perpendicular to the bases in a prism, it is called a right prism. An irregular prism will have an irregularly shaped base that is, the length of the edges will be unequal.īased on the angle between the bases and the faces, there are two prisms: The right prism and the oblique prism. A regular prism will have a regular-shaped polygon as its base that is, the length of the edges will be equal. This information concludes that a hexagonal prism will have hexagonal bases.ĭepending on the shape of the base, a prism can be of two types: Regular prism and Irregular prism. The other faces of a prism can be rectangles or parallelograms. The base is a polygon like a triangle, square, hexagon, etc. The prism is named after the shape of the base. In three dimensions, hexagonal prisms with parallel opposite faces are called parallelohedrons and these can tessellate 3-space by translation.A 3-D solid figure with flat surfaces and two identical bases is a prism. Irregular hexagons with parallel opposite edges are called parallelogons and can also tile the plane by translation. This means that honeycombs require less wax to construct and gain much strength under compression. In a hexagonal grid each line is as short as it can possibly be if a large area is to be filled with the fewest hexagons. Hexagonal structures Giant's Causeway closeupįrom bees' honeycombs to the Giant's Causeway, hexagonal patterns are prevalent in nature due to their efficiency.

Self-intersecting hexagons with regular vertices There are six self-crossing hexagons with the vertex arrangement of the regular hexagon: This pattern repeats within the rhombitrihexagonal tiling.Ī self-intersecting hexagon ( star polygon) This pattern repeats within the regular triangular tiling.Ī regular hexagon can be extended into a regular dodecagon by adding alternating squares and equilateral triangles around it. A regular hexagon can be dissected into six equilateral triangles by adding a center point. A regular hexagon can be stellated with equilateral triangles on its edges, creating a hexagram. The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscribed circle or circumcircle, which equals 2 3. It is bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential (has an inscribed circle). Transfer the line segment AB four times on the circumscribed circle and connect the corner points.Ī regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral and equiangular. When the side length AB is given, drawing a circular arc from point A and point B gives the intersection M, the center of the circumscribed circle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
